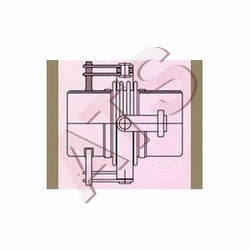
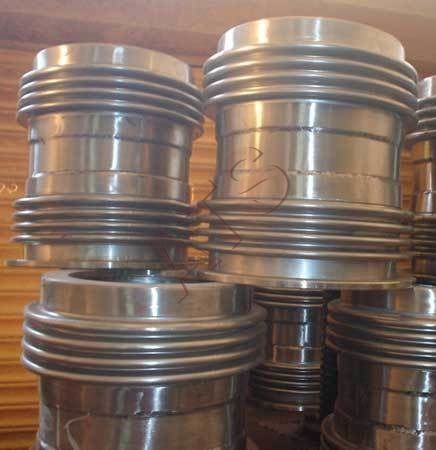
Gimbal Expansion Bellows
Product Details:
- Application For Industrial & Workshop Use
- Feature Easy To Use
- Product Type Other
- Material SS
- Shape Round
- Surface Galvanized
- Size 5-50 Inch
X
Gimbal Expansion Bellows Price And Quantity
- 1 Piece
Gimbal Expansion Bellows Product Specifications
- Other
- Galvanized
- For Industrial & Workshop Use
- 5-50 Inch
- Easy To Use
- SS
- Round
Gimbal Expansion Bellows Trade Information
- Telegraphic Transfer (T/T) Cash in Advance (CID) Cheque Cash Advance (CA)
- 100 Piece Per Day
- 1 Week
- Western Europe Australia North America Eastern Europe Central America Middle East South America Asia Africa
- All India
Product Description
A gimbal expansion bellows is a specialized type of expansion joint used in piping systems to absorb thermal expansion, vibration, and misalignment while maintaining a leak-tight connection. It consists of two bellows units interconnected by a gimbal arrangement, allowing for multi-directional movement. This design provides flexibility in accommodating axial, lateral, and angular movements, making it suitable for applications where pipes are subject to complex motions or where space constraints are present.
FAQ:
Q: What is the purpose of a gimbal expansion bellows?
A: The primary purpose of a gimbal expansion bellows is to compensate for thermal expansion, vibration, and misalignment in piping systems. It absorbs the movement and stress caused by temperature changes, structural settling, or equipment vibrations, preventing damage to the piping and maintaining the integrity of the system.
Q: Where are gimbal expansion bellows used?
A: Gimbal expansion bellows are commonly used in piping systems across various industries, including power generation, petrochemical, oil and gas, HVAC, and industrial processes. They are particularly suitable for applications involving large-diameter pipes, high temperatures, and complex motion patterns, such as in turbine exhaust systems, heat exchangers, or ductwork in buildings.
Q: How does a gimbal expansion bellows work?
A: A gimbal expansion bellows consists of two bellows units connected by a gimbal arrangement, which allows for rotational movement. When the connected piping undergoes axial, lateral, or angular movement due to thermal expansion or vibration, the bellows units flex and accommodate these motions while maintaining a sealed connection. The gimbal arrangement ensures unrestricted movement in multiple directions.
Q: What materials are gimbal expansion bellows made of?
A: Gimbal expansion bellows are typically constructed from materials that offer high flexibility, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance. Common materials include stainless steel, Inconel, and other alloys suitable for the specific application requirements. The material selection depends on factors such as the operating temperature, pressure, corrosive environment, and structural considerations.
Enter Buying Requirement Details
Other Products in 'Expansion Bellows & Joints(S.S Metal) ' category
 |
ATS HYDRAULIC ENGINEERS
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS